By Sam Reid
Trading in the world's largest financial market can seem daunting at first, but with the right foundations, you’ll be well on your way to profitable forex trading.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essential building blocks of forex trading—from terminology and chart reading to indicators and backtesting—so you can approach the market with confidence.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essential building blocks of forex trading—from terminology and chart reading to indicators and backtesting—so you can approach the market with confidence.
Getting to grips with forex trading terms
Before placing your first order, it’s vital to get comfortable with the language of forex trading. Here are key terms to add to your glossary:
Taking five minutes to jot these down and revisit them can save you confusion—and costly mistakes—later on.
- Forex (Foreign Exchange): Buying one currency while selling another.
- Long vs. Short: Long means buying a currency pair, expecting it to rise. Short means selling first, aiming to buy back lower.
- Bullish & Bearish: A bullish market is rising, while bearish is falling.
- Pips (Price Interest Points): The smallest price movement in a currency pair, typically the fourth decimal place. You may also hear “points” or “ticks.”
- Support & Resistance: Horizontal levels where price tends to bounce (support) or reverse (resistance).
- Bid & Ask: The bid is the price your broker will buy from you; the ask is the price they’ll sell to you.
Taking five minutes to jot these down and revisit them can save you confusion—and costly mistakes—later on.
Reading candlesticks and price action
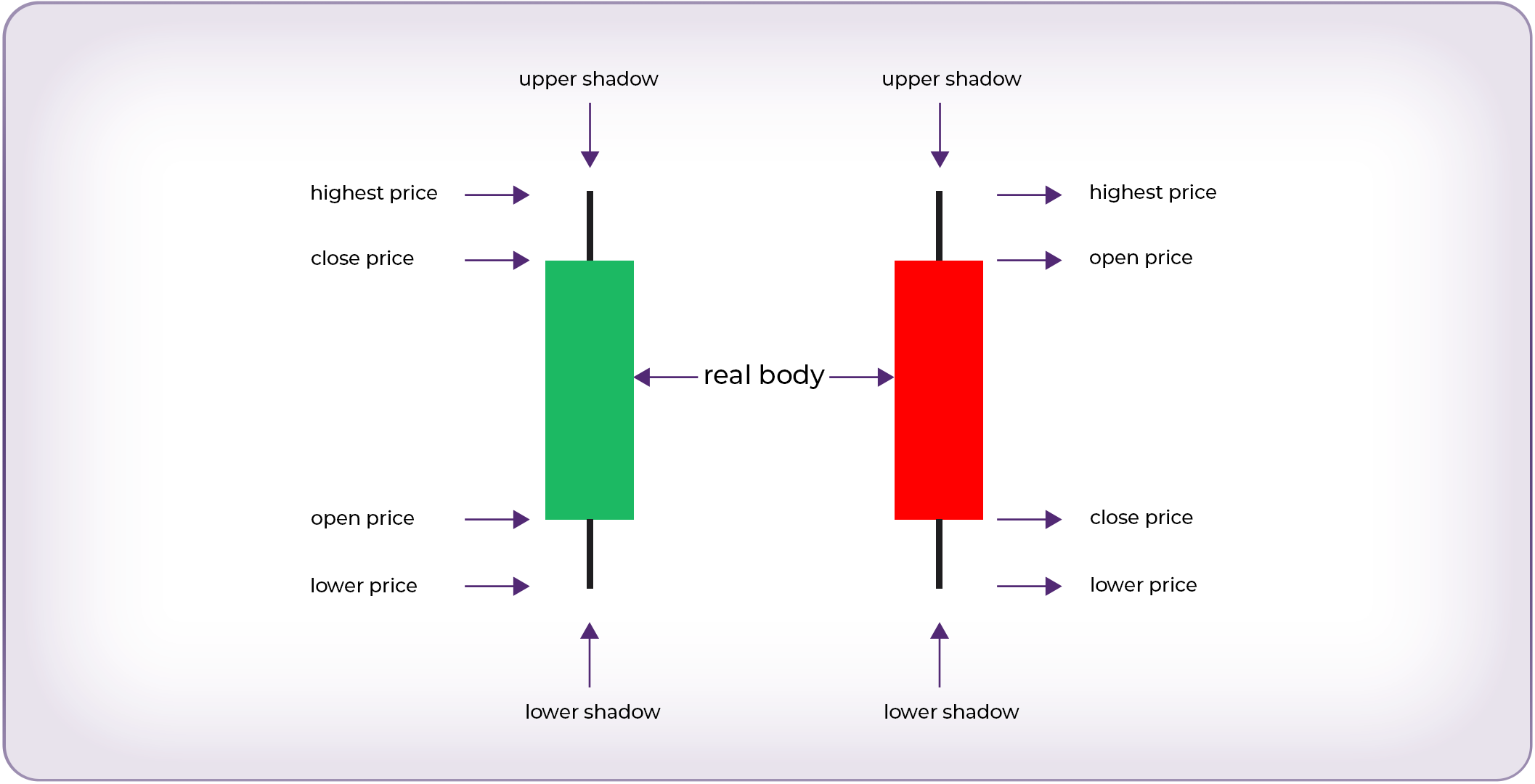
Most traders rely on candlestick charts because each candle packs in four data points: Open, High, Low, and Close (OHLC). Here’s how to interpret them.
Body & Wick: The colored “body” shows open-to-close movement; thin lines (“wicks”) indicate price extremes.
Bullish Candle: Closes higher than it opened—often colored green.
Bearish Candle: Closes lower than it opened—often colored red.
Body & Wick: The colored “body” shows open-to-close movement; thin lines (“wicks”) indicate price extremes.
Bullish Candle: Closes higher than it opened—often colored green.
Bearish Candle: Closes lower than it opened—often colored red.
Candlesticks form patterns that tell stories about market sentiment, like dojis (indecision), engulfing patterns (potential reversal), and hammers/shooting stars at support or resistance levels. As you study live charts, sketch these patterns yourself. Drawing cements your understanding far better than passive watching.
Identifying market trends
A core principle in forex trading is to trade with the trend, not against it. Trends come in three flavors:
Within trends you’ll see runs (extensions) and pullbacks (retracements)—prime spots for entries—and choppy/indecisive periods best avoided.
A simple three-point rule defines a trend: initial high (or low), a pullback, then a new structure high (or low). Everything afterward is a continuation—trade those points for the best odds.
- Bullish trend: a series of higher highs and higher lows
- Bearish trend: a series of lower lows and lower highs
- Consolidation: sideways movement between clear support and resistance
Within trends you’ll see runs (extensions) and pullbacks (retracements)—prime spots for entries—and choppy/indecisive periods best avoided.
A simple three-point rule defines a trend: initial high (or low), a pullback, then a new structure high (or low). Everything afterward is a continuation—trade those points for the best odds.
Key indicators to use
While price action is king, certain lagging indicators add confirmation to trading setups.
Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) is one good example. They are faster-reacting than simple MAs. Use a combination of short, medium, and long EMAs to gauge trend strength.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is another common one. RSI measures momentum and speed of price movements. Overbought/oversold readings can hint at reversals or pullbacks.
You'll also come across MACD (Moving Average Convergence/Divergence) in this category. This one tracks convergence (trend continuation) and divergence (potential reversals) between two EMAs.
No indicator is perfect, but when multiple signals align, you can build high-confidence trade setups.
Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) is one good example. They are faster-reacting than simple MAs. Use a combination of short, medium, and long EMAs to gauge trend strength.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is another common one. RSI measures momentum and speed of price movements. Overbought/oversold readings can hint at reversals or pullbacks.
You'll also come across MACD (Moving Average Convergence/Divergence) in this category. This one tracks convergence (trend continuation) and divergence (potential reversals) between two EMAs.
No indicator is perfect, but when multiple signals align, you can build high-confidence trade setups.
Selecting your trading broker
Choosing a reputable broker is crucial. We recommend Exness for its ultra-low spreads, robust regulation across multiple jurisdictions, lightning-fast execution, and a user-friendly trading platform. Whether you’re on desktop or mobile, Exness delivers the tools and support forex beginners need to start on the right foot.

Building a solid trade plan
A trade plan is your rulebook for entering, managing, and exiting positions. It transforms trading from emotional guessing to a disciplined process. Key components include:
Stick to your plan. If a setup fails to tick all your boxes, skip it. Over time you’ll refine the plan, dropping unprofitable rules and adding new filters.
- Strategy definition: Clear entry and exit rules you’ve tested.
- Watch list: A shortlist of currency pairs that meet your criteria.
- Portfolio: All pairs you’ve backtested and deemed reliable enough for live trading.
Stick to your plan. If a setup fails to tick all your boxes, skip it. Over time you’ll refine the plan, dropping unprofitable rules and adding new filters.
Choosing your time frame
Your lifestyle dictates your ideal chart time frame:
Daily charts are best for beginners or busy traders where they would usually review once or twice per day. 4-hour and 1-hour charts require more screen time but reveal additional entry points.
Daily charts are best for beginners or busy traders where they would usually review once or twice per day. 4-hour and 1-hour charts require more screen time but reveal additional entry points.
Master the daily time frame first to reduce noise and focus on the big picture. Later, you can apply the same principles to shorter windows when you have more availability.
Backtesting your strategies
Backtesting means testing your rules on historical data to see if they produce a profit. A simple spreadsheet might include:
| Pair | Time Frame | Strategy Name | Entry Date/Time | Entry Price | Stop-Loss | Target 1 | Target 2 | Exit Date/Time | P&L | Notes |
Tracking every detail, including screenshots, builds your mental confidence. Consistent returns on past data make you less likely to second-guess your plan in real time.
| Pair | Time Frame | Strategy Name | Entry Date/Time | Entry Price | Stop-Loss | Target 1 | Target 2 | Exit Date/Time | P&L | Notes |
Tracking every detail, including screenshots, builds your mental confidence. Consistent returns on past data make you less likely to second-guess your plan in real time.
Putting it all together
- Learn & define: master terminology, candlesticks, and market structure
- Plan & select: create your trade plan, watch list, and portfolio
- Confirm with indicators: use EMAs, RSI, and MACD as secondary checks
- Choose your time frame: start with daily, then expand to 4-hour/1-hour
- Backtest & refine: rigorously test on past data, tweak rules, and repeat
Follow these points like grounding yourself in the basics, making a disciplined plan, and validating your strategy through backtesting, and you’ll lay a rock-solid foundation for consistent results in forex trading.
Remember: consistency and patience are your greatest allies. Good luck!
Forex trading FAQs
What is forex trading?
Forex trading involves buying one currency against another, profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. It’s the world’s largest market by daily volume.
How much money do I need to start forex trading?
You can open a micro account with as little as $100–$200, but a more realistic starting balance is $500–$1,000 to manage risk effectively.
Which time frame is best for beginners?
The daily chart is ideal for new traders. It offers clear trend signals and requires minimal screen time—perfect for those balancing trading with other commitments.
What is a pip in forex trading?
A pip is the smallest unit of price movement—typically the fourth decimal place (0.0001) in most currency pairs.
How do I manage risk in forex trading?
Use stop-loss orders, stick to your trade plan, risk only 1–2% of your capital per trade, and diversify across a portfolio of pairs.
Which broker should I choose for forex trading?
We recommend Exness for its competitive spreads, strong regulation, fast execution, and intuitive platform—ideal for both beginners and experienced traders.
Forex trading involves buying one currency against another, profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. It’s the world’s largest market by daily volume.
How much money do I need to start forex trading?
You can open a micro account with as little as $100–$200, but a more realistic starting balance is $500–$1,000 to manage risk effectively.
Which time frame is best for beginners?
The daily chart is ideal for new traders. It offers clear trend signals and requires minimal screen time—perfect for those balancing trading with other commitments.
What is a pip in forex trading?
A pip is the smallest unit of price movement—typically the fourth decimal place (0.0001) in most currency pairs.
How do I manage risk in forex trading?
Use stop-loss orders, stick to your trade plan, risk only 1–2% of your capital per trade, and diversify across a portfolio of pairs.
Which broker should I choose for forex trading?
We recommend Exness for its competitive spreads, strong regulation, fast execution, and intuitive platform—ideal for both beginners and experienced traders.
Disclaimer: Remember that forex and CFD trading involves high risk. Always do your own research and never invest what you cannot afford to lose.



