Summary
Momentum can turn a quiet chart into a fast moving opportunity. This guide walks beginners through what momentum trading is, how it works, the indicators that help confirm trend strength, and the momentum trading strategies used by traders around the world. You will also learn how professionals analyse volume and volatility, how to enter and exit with discipline, and how traders avoid common mistakes like chasing prices or confusing noise with genuine momentum. A real world example from the Nasdaq AI rally shows how momentum trading plays out in practice.
What Is Momentum Trading?
Momentum trading is a style of trading where you buy an asset that is rising with strength or sell an asset that is falling with strength. Traders take advantage of the continuation of price trends rather than trying to predict reversals or guess bottoms.
The logic is straightforward. Strong stocks often stay strong for a while. Weak stocks often stay weak for a while. Traders identify that strength and ride the movement until momentum slows.
Momentum trading focuses on:
- Trend acceleration
- Volume confirmation
- Clear direction
- Fast entries and disciplined exits
Instead of relying on long term fundamentals, momentum trading places most of its weight on price action. Traders want movement, not stagnation.
Key Takeaways
- Momentum trading is built around trend continuation.
- Traders aim to capture the middle of a move rather than the start or the end.
- Strength, not value, is the core driver of decisions.
- Volume confirmation is essential to avoid false signals.
- Momentum trading works best when markets are active and directional.
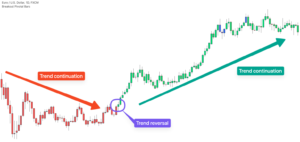
How Momentum Works
Momentum is the speed behind a trend. When price begins to accelerate, more traders begin to watch that market. Their participation increases the strength of the move. As long as buying or selling pressure remains high, the trend keeps moving.
Momentum is influenced by three foundational elements.
Volume
Volume measures how many units of an asset are being traded. Momentum trading depends heavily on strong volume. If volume is weak, price movements are less reliable and more prone to sudden reversals.
High volume tells you that a large number of traders agree on direction. Low volume often indicates hesitation and can make momentum trading more risky.
Volatility
Momentum traders rely on volatility because it creates the energy behind the move. Higher volatility means stronger price swings and more opportunities. Without enough volatility, trends may not extend far enough to generate meaningful trades.
Time Frame
Momentum trading can be applied to any time frame.
- Day traders may use one minute or five minute charts.
- Swing traders may use four hour or daily charts.
- Longer term traders may base trades on weekly or monthly momentum.
How to Trade Momentum
Learning how to trade momentum begins with understanding what makes a strong setup.
The steps include:
- Identify a clear trend with strong direction.
- Confirm the trend with volume and momentum indicators.
- Enter after a clean pullback or breakout.
- Set a stop loss to protect the account.
- Ride the trend until momentum begins to weaken.
Momentum trading requires balance. Traders must react quickly but must also avoid emotional decisions. Many beginners enter trades too late after the move has already expanded dramatically. Others enter without confirmation and get caught in false breakouts.
Structured risk management helps avoid these errors. A platform like AvaTrade provides advanced charting tools that help traders track trend strength, apply momentum trading indicators and practice spotting clean setups before risking real capital.
Momentum Trading Indicators
Momentum trading indicators help traders measure the strength and direction of price movement. These tools support decision making but should never replace price action itself.
Momentum Indicator
The momentum indicator compares the current closing price to a previous closing price. If the line rises, momentum is increasing. If the line falls, momentum is weakening.
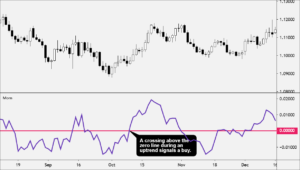
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI moves between 0 and 100 and shows when a market may be overbought or oversold.
(Traditional Oversold and Overbought RSI zones)
Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data and help traders see whether the market is trending. A short moving average rising above a longer one suggests upward trend strength.
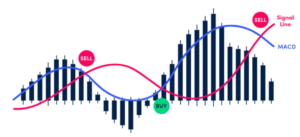
Stochastic Oscillator
The stochastic oscillator measures the speed of price movements relative to recent ranges.
Momentum Trading Strategies
There are several effective momentum trading strategies that beginners can apply with practice.
1. Breakout Strategy
You enter when price breaks above resistance or below support with strong volume.
2. Trend Following Strategy
You follow the trend by entering after minor pullbacks in the direction of the main movement.
3. Moving Average Crossovers
This strategy uses fast and slow moving averages to signal potential continuation.
4. Relative Strength Strategy
You compare the performance of one asset against another to find stronger candidates.
Elements of a Successful Momentum Approach
Momentum trading thrives when traders follow a structured approach. These elements guide success:
- Choosing the right assets with strong trend potential
- Timing entries only when the trend has confirmation
- Managing positions with awareness of spreads and volatility
- Setting profit targets and stop losses before entering
- Respecting exit rules even when emotions interfere
Historical Example: Nasdaq AI Momentum Rally (2023)
A clear real world illustration of momentum trading appeared during the AI driven rally in 2023. According to CNBC, Nvidia, Meta and other AI related stocks helped power the Nasdaq to gains above 40 percent for the year.
Strong volume supported the rally. Pullbacks were shallow because buyers rushed in. Short sellers struggled because the momentum kept carrying prices higher.
A momentum trader watching this trend would have seen:
- Continuous higher highs
- Strong volume spikes
- Positive RSI readings
- Clear upward moving averages
Common Beginner Challenges
Momentum trading attracts beginners, but many face similar obstacles. New traders often enter too late, chase price after dramatic moves or rely on emotions rather than confirmation.
Beginners may ignore volume or depend entirely on indicators. Low volume moves reverse frequently and indicators should confirm decisions instead of dictating them.
Over-leveraging is another danger. Large positions in fast markets can wipe an account quickly. Setting stop losses, understanding risk to reward ratios and maintaining strict discipline are essential.
Education, paper trading and small position sizes help beginners avoid these common mistakes.
Practical Examples of Momentum Trading
Imagine an asset breaking above resistance after weeks of sideways movement. Volume rises and the RSI increases. This is a classic momentum trading entry.
In a downtrend, a stock breaks below support with heavy selling. Traders enter short positions and exit when selling pressure fades.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Momentum Trading
Momentum trading offers clear benefits such as fast opportunities during strong trends and frequent setups across different markets.
It also has drawbacks including rapid reversals, emotional risks and whipsaw movements. It requires monitoring and a disciplined mindset.
Navigating Risks in Momentum Trading
Risks in momentum trading come mainly from sharp reversals. Unexpected news or volume shifts can end a trend instantly. This is why stop losses matter.
Whipsaws also appear in momentum trading. Avoiding them requires confirmation, volume checks and patience.
Conclusion
Momentum trading is a dynamic trading approach that teaches traders how to recognise strength, follow the trend and exit with discipline. Tools like RSI, moving averages and volume analysis play an important role in the strategy. Real examples such as the Nasdaq AI rally show how powerful momentum can become when multiple forces align.
By practising consistently and managing risk carefully, beginners can develop a structured approach to momentum trading. Platforms such as AvaTrade help traders apply what they learn in a controlled environment.
Momentum trading is about reading strength in the present and reacting with structure. With discipline and preparation it can become a valuable strategy for traders worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 types of trading?
The four common types of trading are day trading, swing trading, position trading and scalping. Each style differs by holding period, risk appetite and strategy structure.
What is the difference between swing trading and momentum trading?
Swing trading focuses on capturing medium term moves within a broader trend. Momentum trading focuses on strength and speed of price movement, often reacting to acceleration rather than general trend structure.
How long is momentum trading?
Momentum trading can last from minutes to several weeks depending on the strength of the trend, the market involved and the trader’s timeframe. The key factor is trend continuation rather than fixed duration.
What is the difference between momentum trading and trend trading?
Trend trading focuses on overall direction of the market, even during slower periods. Momentum trading focuses specifically on the strongest sections of the trend where speed and volume are high.

 17th Nov 2025
17th Nov 2025