Introduction: What is Risk Return Trade Off?
The risk return trade off explained in its simplest form means that greater rewards come with greater risks. If an investor wants the possibility of high profits, they must also accept the chance of larger losses. On the other hand, investments that provide more stability usually deliver smaller returns. This principle is central to all of finance, from day trading to long-term retirement planning.
Every investor, whether a beginner in stocks or a professional fund manager, encounters the same question: how much risk am I willing to accept for the return I expect? Answering this effectively is the foundation of portfolio building and wealth growth.
Why the Risk Return Trade Off Matters
- Setting realistic expectations: It clarifies that doubling your money in a year is unlikely without taking significant risk.
- Building discipline: It forces investors to think about downside potential rather than chasing returns blindly.
- Portfolio design: It guides asset allocation decisions, balancing equities, bonds, and other instruments.
- Risk management: It underlines that losses are as much a part of investing as gains, which helps traders prepare psychologically and financially.
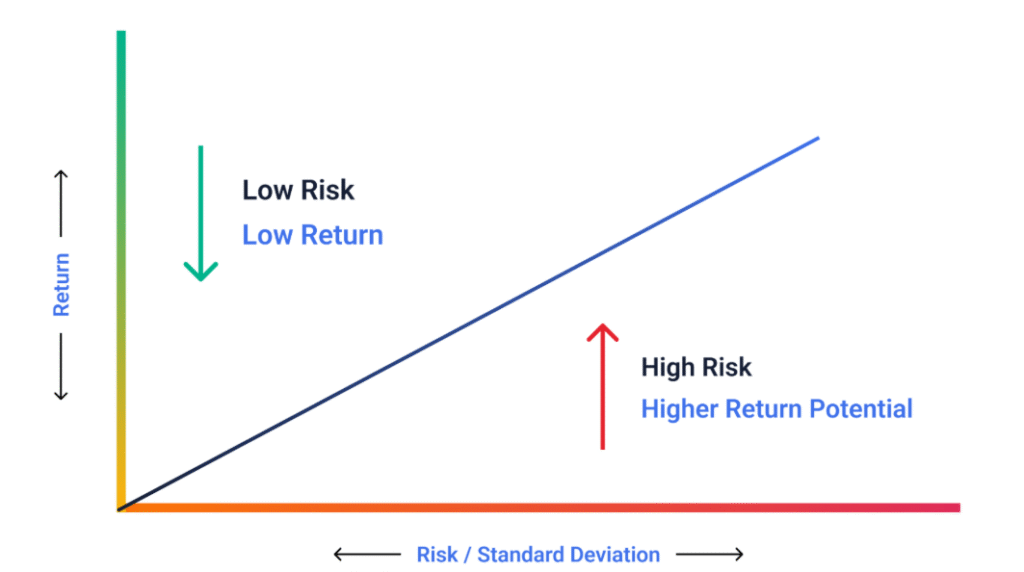
Risk vs Return: The Core Principle
The relationship of risk vs return is simple in theory but complex in practice. A penny stock might promise huge potential gains but also carries the risk of losing the entire investment. In contrast, a government bond provides security but with much smaller returns.
For traders, this is not just theory. When speculating on currency pairs or equities, a high leverage position can magnify both profits and losses. The same principle applies whether investing in mutual funds, commodities, or crypto.
Understanding Risk and Return in Context
The Role of Risk Tolerance
Every investor has a unique risk tolerance shaped by factors such as income, age, financial goals, and personality. A young trader with a stable job might be comfortable with short-term volatility, while someone nearing retirement will usually prefer stability.
Assessing your own tolerance is critical. Without this step, portfolios may be mismatched to your comfort level, leading to panic selling during downturns.
Investment Horizon
The length of time an investor plans to hold an investment changes the trade off. Short-term trading often requires handling more volatility. Long-term investing in equities, however, allows time for markets to recover from downturns and compound returns over decades.
How to Balance Risk and Return
- Asset Allocation: Splitting investments across equities, bonds, commodities, and alternative assets ensures no single class dominates portfolio risk.
- Diversification in Investing: Within each asset class, spreading exposure across sectors or regions reduces concentration risk.
- Modern Portfolio Theory: This framework suggests investors can achieve the best possible return for a given level of risk by combining uncorrelated assets. It mathematically shows how diversification moves a portfolio onto the efficient frontier where returns are maximised relative to risk.
Risk Return Trade Off in Investing
The trade off applies differently depending on the type of investment:
- Equities: Offer high growth potential but are vulnerable to volatility.
- Bonds: Provide steady returns with lower risk, making them attractive to conservative investors.
- Mutual Funds: Blend equities and debt to provide different risk profiles.
- ETFs: Track markets or sectors, giving investors targeted exposures.
- Alternative assets: Commodities, crypto, or real estate carry unique risk factors and potential rewards.
Risk Return Trade Off Examples
| Investment Type | Risk Level | Return Potential | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Bonds | Low | Low | Steady annual interest, low chance of loss |
| Equities | Medium to High | Medium to High | Stock market gains over 5–10 years |
| Equity Mutual Funds | Medium | Moderate to High | Diversified portfolio across sectors |
| Leveraged ETFs | High | High | Amplified gains or losses in short term |
| Cryptocurrency | Very High | Very High | Sharp price swings, speculative but potentially lucrative |
How Risk Return Trade Off is Calculated
Sharpe Ratio
The Sharpe ratio measures excess return over the risk-free rate per unit of volatility. A higher Sharpe ratio means better risk-adjusted returns.
Beta Coefficient
The beta coefficient measures how much an asset moves compared to the market benchmark. A beta of 1 means it tracks the market closely, greater than 1 indicates more volatility, and less than 1 means less volatility.
Alpha
Alpha measures performance above or below a benchmark. A positive alpha indicates outperformance, while negative alpha means underperformance.
Risk Return Trade Off in Mutual Funds
Mutual funds illustrate the trade off clearly. Equity funds carry higher risk but greater growth potential. Debt funds are safer but lower-yielding. Hybrid funds try to strike a balance. Investors use metrics like Sharpe, alpha, beta, and standard deviation to evaluate whether a fund’s returns are worth the risks.
Investment Risk Management
- Setting stop-loss levels in trading accounts.
- Avoiding overexposure to a single sector or stock.
- Keeping emergency cash to prevent forced selling.
- Rebalancing portfolios regularly to maintain target allocation.
Practical Risk Return Trade Off Examples for Traders
- Forex trading: Leverage increases both potential profit and loss.
- Options trading: Buying calls offers high upside but can result in a complete loss of premium.
- Commodity investing: Gold tends to offer stability, while oil can swing dramatically.
FAQs
What is the risk-return trade-off also known as?
It is also referred to as the risk-reward trade-off, meaning the balance between the potential risk of an investment and its expected return.
What is the risk-return trade-off in CAPM?
In the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), the trade-off is expressed as the relationship between expected return and systematic risk, measured by beta.
What is the risk-return tradeoff chart?
It is a visual graph plotting risk on the x-axis and return on the y-axis, often showing the efficient frontier of optimal portfolios.
What is the risk trade-off analysis?
It is the process of comparing different investment opportunities by weighing their potential risks against possible returns using metrics like Sharpe ratio, beta, or standard deviation.
Conclusion
The risk return trade off explained is one of the most fundamental principles in investing. It reminds us that there is no free return. Every opportunity comes with some degree of risk, and the art of investing lies in balancing that risk with potential reward. By applying concepts like diversification in investing, asset allocation, modern portfolio theory, and tools such as the Sharpe ratio and beta coefficient, traders and investors can build portfolios that suit their own risk tolerance.
Ultimately, the goal is not to eliminate risk but to manage it intelligently. With a thoughtful approach, the risk-return trade off becomes a roadmap for achieving long-term financial growth while avoiding the pitfalls of unmanaged exposure.
 Sam Reid Staff Writer
Sam Reid Staff Writer 25th Aug 2025
25th Aug 2025