Low Spread Forex Brokers: Why They Matter for Traders
 Sam Reid Staff Writer
Sam Reid Staff Writer
In forex trading, every pip has an impact. Yet many traders overlook one of the most consistent costs that affects every trade they make: the spread. While some brokers promote their tools, welcome bonuses, or commission-free trades, the spread is the quiet cost that takes a cut the moment a position is opened.
A 2023 study by ForexBrokers.com reported that top brokers averaged spreads of 0.1 to 1.0 pips on EUR/USD, while less competitive ones charged more than 2.5 pips. This difference, while it might seem small, adds up quickly. Traders who understand how spreads affect performance are better positioned to preserve their capital and make smarter decisions.
Let’s explore what spreads are, why they matter, and which brokers provide some of the most competitive trading conditions today.
What Is a Spread in Forex?
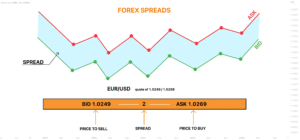
A spread is the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) price of a currency pair. It is one of the main ways brokers earn revenue. For traders, it represents an unavoidable cost. Every time a position is opened, it begins with a negative balance equal to the size of the spread.
For example, if EUR/USD has a bid of 1.1000 and an ask of 1.1002, the spread is 2 pips. A trader buying at 1.1002 must wait until the price increases past that level just to break even.
Even a small increase in the spread affects how quickly a trade becomes profitable. This is especially important for strategies like scalping, where tight entry and exit levels are used.
(Calculating spreads in trading)
Why Spreads Are More Critical Than They Appear
Some traders pay little attention to spreads when choosing a trading broker. However, spreads directly reduce profitability. If you trade frequently, the costs pile up. For example, trading one standard lot with a 2-pip spread costs $20 per trade. Multiply that by 100 trades, and the monthly spread cost reaches $2,000.
Now imagine the same trades at a 0.5-pip spread. That’s a $1,500 saving over the same number of trades. The difference is measurable and significant. This is why competitive spreads should be one of the top considerations when evaluating brokers.
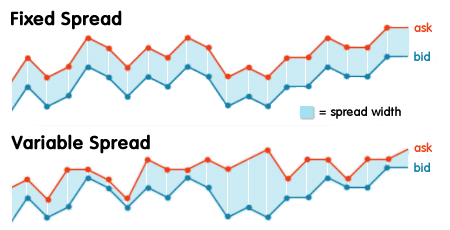
Fixed vs Variable Spreads
Brokers typically offer two types of spreads:
-
Fixed spreads remain the same under normal and volatile conditions. This provides cost stability.
-
Variable spreads change based on market liquidity and volatility. During high activity periods, they tend to tighten. During uncertainty or low volume, they can widen sharply.
Each type suits different trading styles. Fixed spreads are useful for swing traders or those who want predictable costs. Variable spreads benefit traders who operate during high-volume sessions and want lower average entry costs.
(fixed-vs-variable-spread illustrated)
Low spread forex brokers uae
For traders based in the UAE, finding reliable brokers with low spreads and strong trading infrastructure is essential. Here are three brokers trusted by active traders in the region:
Exness
Known for some of the tightest spreads in the industry, Exness offers raw spread accounts starting from 0.0 pips. The broker supports both MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5, offers instant execution, and is popular among scalpers and professional traders. Exness is licensed in multiple jurisdictions and offers support in Arabic.
XTB
With its proprietary xStation platform, XTB provides low spreads on major pairs like EUR/USD and USD/JPY. Spreads during peak hours are often between 0.1 and 0.5 pips. The platform includes market sentiment tools, educational content, and fast execution for retail traders.
Avatrade
Offering fixed and floating spread options, Avatrade is a good choice for swing traders and position traders. Spreads are competitive, especially when holding trades overnight. The broker is regulated in several regions and offers localized support for traders in the Gulf.
All three brokers provide favorable trading conditions with tight spreads. UAE traders using these platforms gain access to better pricing and improved trade execution.
When Spreads Widen
Spreads widen during certain market conditions. Low liquidity, major economic releases, or unexpected global events can all increase the spread. These events include central bank rate announcements, inflation reports, or geopolitical shocks.
Some brokers maintain relatively stable spreads even in volatile times. Others widen them significantly. Traders should be aware of how their broker behaves during news events. Platforms that display live bid and ask prices help traders monitor these changes in real time.
Account Types and Spread Impact
Most brokers offer multiple account types, each with different cost structures. The two most common are:
-
Standard accounts, where spreads are wider but there are no separate commission charges.
-
Raw or ECN accounts, where spreads are tighter and a small commission is applied per trade.
High-frequency traders usually benefit from raw spread accounts. Casual traders may prefer standard accounts to avoid commission costs. Traders should compare both options based on how often they trade and their average position size.
Spread Costs in Practice
Let’s say you trade the GBP/USD pair on a standard account with a 2-pip spread. On a single standard lot, that’s a $20 cost per trade. Over 100 trades, that’s $2,000.
Switch to a raw spread account where the spread is 0.5 pips, and commission is $7 per round trip. Now each trade costs about $12 in total. Over 100 trades, that’s $1,200. The choice of account affects your monthly profitability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One mistake traders make is assuming the lowest possible spread always means the best deal. A broker might offer near-zero spreads but charge high commissions or slow down order execution.
Another mistake is trading during off-hours. Liquidity drops during Asian sessions and weekends, which leads to wider spreads and more erratic price movements.
To control costs, traders should:
-
Avoid trading during low-volume periods.
-
Choose sessions with the highest liquidity, like the London and New York overlap.
-
Use brokers that offer transparent pricing and stable execution.
What Else Affects the Cost Per Trade?
Spreads are just one part of the total trading cost. Other factors include:
-
Commissions: Some accounts add a fixed fee per trade.
-
Swap rates: These are overnight charges for holding positions.
-
Slippage: The difference between the expected price and executed price.
-
Platform fees: Some brokers charge for tools or market data.
The goal is to find a broker that balances low spreads with fair commission structures, fast execution, and no hidden fees.
Why Regulation Still Matters
Cost efficiency is important, but so is safety. Brokers regulated by authorities such as the UK’s FCA or the UAE’s SCA must meet strict standards. They are required to segregate client funds, offer negative balance protection, and comply with clear reporting practices.
While regulation alone doesn’t guarantee low spreads, it adds an important layer of trust. A well-regulated broker that also provides tight spreads offers the best overall value.
Final Advice for Traders
Spreads should be treated as a core trading cost. Reducing this cost improves risk-reward ratios, strengthens strategy results, and creates more room for profit.
Choosing the right trading broker is part of building a sustainable strategy. Whether you focus on intraday moves or long-term setups, spread size affects how every trade plays out.
FAQs
What is the main advantage of a low spread in forex?
A low spread reduces the cost of entering and exiting trades. This means traders can reach break-even faster and retain more profit per trade.
Is it better to trade with lower or higher spread?
Lower spreads are more cost-efficient. They reduce transaction costs and improve strategy performance, especially for high-frequency or short-term trades.
Is it possible to trade forex without spread?
Some brokers offer zero spread accounts. These accounts remove the bid-ask difference but charge a commission per trade instead. The cost still exists, just in another form.
How do spreads affect forex trading?
Spreads influence how quickly trades become profitable. Wider spreads require more price movement to reach break-even and can reduce the effectiveness of certain strategies.
Disclaimer: Remember that forex and CFD trading involves high risk. Always do your own research and never invest what you cannot afford to lose.
 02nd Aug 2025
02nd Aug 2025